Introduction
Marketing is a management tool of any business aiming to enhance sales and incomes. Marketing starts with deciding what to produce based on the requirements of the market. The market, in this case, refers to the person(s) or organisations who demand the products on offer for consumption, further selling or processing. Knowing the target market or markets is an extremely important factor critical to successful marketing. Traditionally, farmers and their facilitators focus on increasing production on farms and then look for markets to sell what is produced, instead of producing what the market wants. The adoption of a marketing strategy requires a farm to shift their focus from ‘producing for the market’ to ‘producing what the customers want’. The decision to produce according to market requirements is an important marketing step as it involves a commitment to specific customer needs, such as type of product, quality and quantity.
The marketing process starts with research to understand what the customers want and goes through the process of developing and offering products that will meet and satisfy customer expectations.
Constraints to agricultural market development in Africa
A number of constraints can be identified as hindering the development of agricultural markets in Africa:
Limited access to information and market support services - In general, there is limited access to useful and sufficient information at the time when farmers need it to make informed production decisions. Such information includes produce prices, market demand in terms of quantity and quality requirements. National agricultural programmes mainly focus on increasing production and marketing support is almost completely neglected. This problem is aggravated by the limited marketing expertise among public extension officers.
Scattered distribution of producers - Most farmers are small-scale and work independently, producing very limited quantities of any particular product. The cost of collecting and consolidating such small quantities into marketable quantities is a big hindrance.
Poor infrastructure - The biggest portion of agricultural production is located in rural areas, which are inaccessible due to poor transport and communication connections. Limited storage facilities also remain a hindrance in most areas.
- Limited production capacity of farmers - Many farmers see marketing as a secondary activity. They put more focus on producing for their home requirements and any extra is then provided to the market. This lack of market focus normally results in farmers having too much unwanted produce. In such situations, farmers become desperate and are forced to sell at ’give-away’ prices.
- Poor undeveloped markets - Lack of an official grading system and quality control standards leads to varying qualities of the same product, making marketing very difficult. Farmers also deal with a variety of buyers of their produce including brokers/middle men, wholesalers, retailers, or consumers, from whom they may receive no feedback. In such cases, there are limited opportunities for improvement or adoption of new ideas.
- Low innovation potential among actors involved in market chains - Market chains have mainly the function to link production with consumption, ensuring that products are somehow marketed. Nevertheless, the communication among market chain actors aiming to respond better to consumer needs is weak. This hampers collaborative efforts along market chains that generate additional consumer value through product differentiation.
- Low public awareness for quality products - Since the purchasing power in most African countries is limited, little has been invested in public awareness campaigns to promote high quality products. However, as the retailing business is growing fast through the rapid expansion of supermarkets, it is expected that public awareness and promotion for quality products will increase in the coming years.
This module provides tools that can be communicated to farmers in training sessions so that they can become more actively involved in marketing activities, without compromising their domestic food requirements. Various approaches, that can be adapted according to the local conditions, are presented here. These approaches have proven successful in increasing farmer participation in marketing activities.
Group discussion: Constraints and challenges of marketing
Create groups of 3 participants and let them discuss the following questions:
- What are your constraints for selling products from your farm?
- How can you communicate a quality product such as ‘organic’?
- How is your access to customers that are interested in organic products
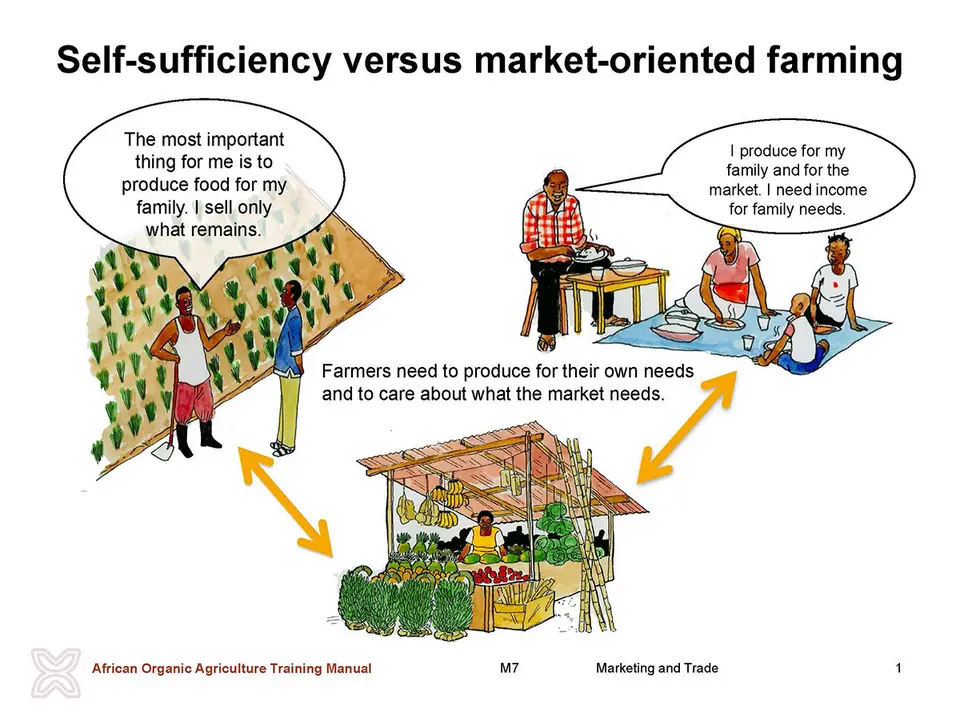
General discussion: Self-sufficiency versus market-oriented farming
Engage the participants in a brainstorming discussion using the following:
- What is the main consideration when choosing the crops to grow: the food for the family, the market or both?
- What makes you change from one crop or enterprise to another?
- Is it possible to combine production for self-sufficiency and the market? What are the opportunities and challenges of combining both?
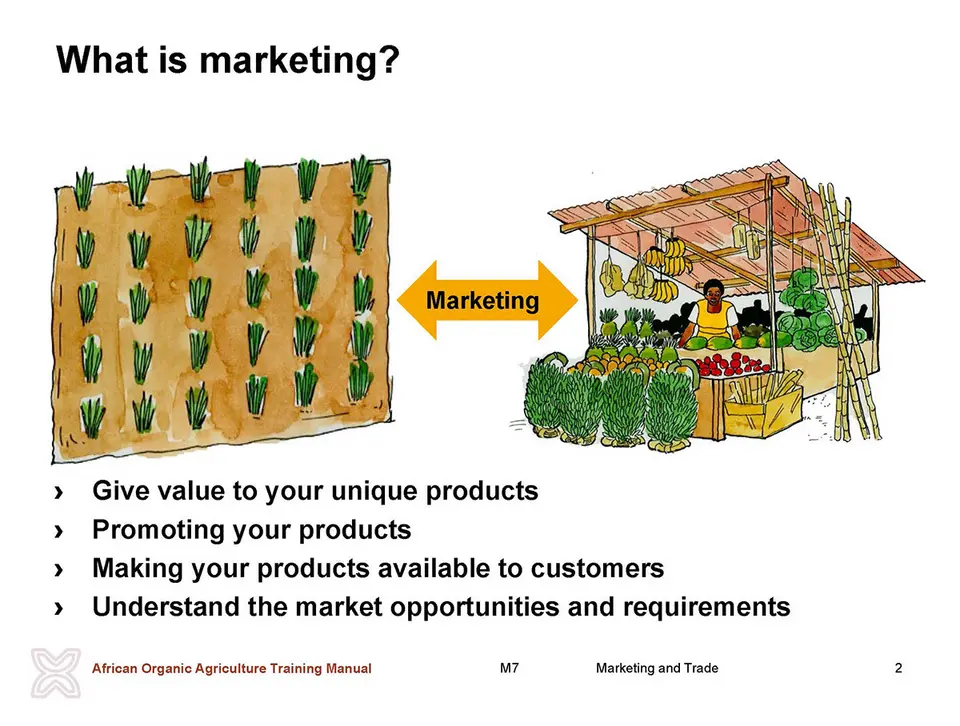
Why is marketing important?
Marketing is important for any business to be able to sell and obtain income. Where ‘farming is treated as a business’, marketing becomes indispensable. This implies that farmers should unquestionably grow crops for which they only expect to gain sufficient income according to the requirements of the different buyers: traders, retailers, or consumers.
Marketing serves as the bridge between farmers and customers, in the farmers’ endeavour to obtain proper knowledge of the expected demand from the market and prices in order to decide what to produce with the aim to improve their incomes and livelihoods. In order to successfully benefit from the opportunities of the market, it is necessary to understand the market (local, domestic or export) and prepare well for it.
For organic products, marketing is especially important as the higher value and sometimes price of organic products often needs to be explained accordingly to customers. Marketing ensures that these values are well communicated, whether face-to-face or through promotion material, in order to boost demand and develop new markets. Tips on how to develop a marketing strategy for organic products and how to efficiently communicate the ’organic values’ are discussed in this module.
Key issues relating to marketing
Marketing involves a series of different complementary activities all aiming to promote and make the required products available to customers. Thus, marketing involves the following issues:
- Research activities: to assess what the requirements of the market are.
- Promotion activities: to promote products including additional services to consumers, to motivate them to purchase.
- Selling activities: determination of how to deliver products to the customer and the product prices.
All these activities are integrated into a process through which a farm or business builds strong customer relationships. Through this process, it creates value for those who are buying the products. Above all, marketing is used to satisfy the customer. Since the customer requirements are continuously changing and because new competitors continuously enter the market, marketing should be a continuous process of monitoring the market and the customer for any new changes.
All in all, marketing involves deciding what to produce on a farm and connecting this with who will buy it. Any decision about what to produce is deeply linked to the ability to sell it. That is, always try to ensure there is a market for whatever a farmer or farmer group will produce before beginning. Knowing the target market or markets is an extremely important factor critical to successful marketing. There are of course other essential factors that need to be taken into consideration when deciding what to grow, such as soil qualities, the climate, knowledge and possibilities for investments in new crops and techniques. These factors are covered in other parts of this manual and can help when deciding what is appropriate to grow under certain conditions.
Discussion: Understanding of marketing
Assess the participants understanding of marketing by asking the following questions:
- Why is marketing necessary?
- How are you involved in marketing?
- Do you have products that are required by the market?
- How do you know that there is a demand for your products?
- Do you have products that are required by the market?
Yearbook on Organic Agriculture in Africa
The website https://statistics.fibl.org/africa.html provides access to various tools that show the current state of organic farming in Africa as a whole, in the five regions and in each country.
Different versions of the Yearbook
- Yearbook on Organic Agriculture in Africa 2023: This yearbook includes short explanatory texts, tables, and dashboards on key indicators (organic agricultural land, organic share of total agricultural land, number of producers, total exports) and key crops and commodities (agricultural land area and exports) for Africa as a whole and its regions. Additionally, for each country, tables and graphs with the key data are available. Please note that while the 2022 data on organic agriculture worldwide are available, these data have not been compiled for Africa as the 2021 data have been.
- The World of Organic Agriculture 2024 contains global data on organic farming, including data from Africa.
- Interactive infographics on key indicators, crops, and exports
- Interactive tables on key indicators, crops, and exports
Data sources
The data shown were provided by FiBL, based on its annual survey on organic agriculture worldwide, which has been conducted since 2000 with the support of the Swiss State Secretariat for Economic Affairs (SECO), IFOAM – Organics International, the Coop Sustainability Fund, and NürnbergMesse. GIZ supported the present Africa-specific compilation within the framework of the Knowledge Centres for Organic Africa (KCOA) project.
 tap and then scroll down to the Add to Home Screen command.
tap and then scroll down to the Add to Home Screen command.