Introduction
Beekeeping describes the skill of keeping bees for income and food. Beekeeping offers a good opportunity for farmers to start up a small-scale business. Bees produce several products including honey, beeswax, pollen, propolis, royal jelly and venom, which all have various applications. The demand for bee products is increasing at the national and international level. In addition, beekeeping benefits the environment and agricultural crops. It does it in the following ways:
- Pollination of agricultural crops: Bees play an important role in the pollination of many flowering plants and crops. They improve yields and quality of both field and horticultural crops. They are of special importance in coffee, cocoa, mango and avocado.
- Conservation of biological diversity: Pollination of wild plants increases their seed production and thus contributes to their maintenance and to conservation of natural biodiversity.
Challenges related to beekeeping in Africa
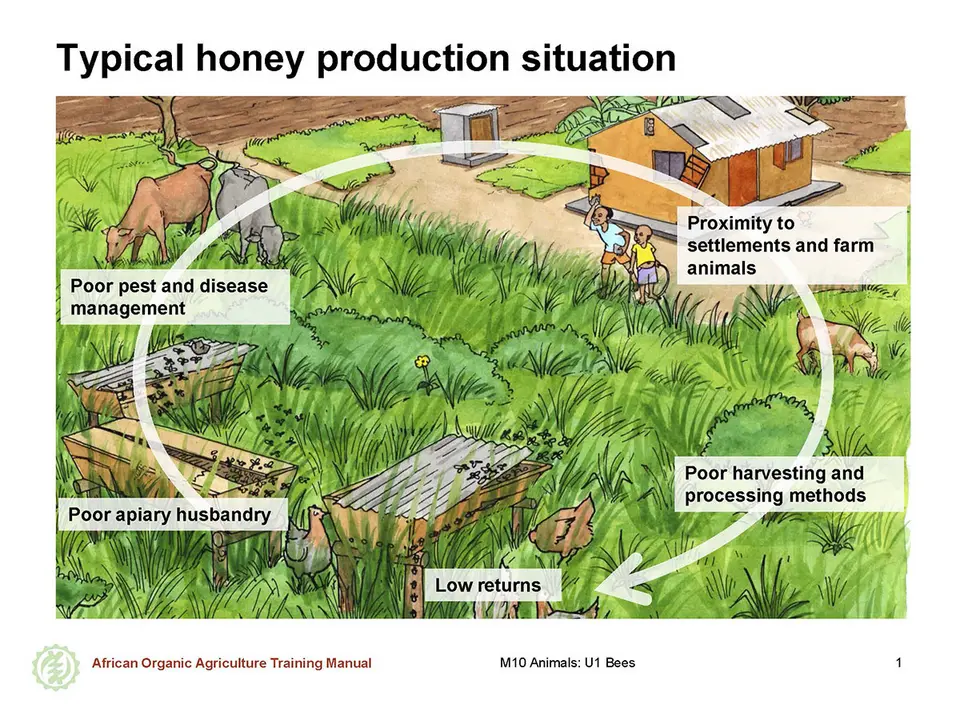
African honey is in demand within Africa and around the world. However, both local and export demand are not sufficiently met due to the highly erratic supply. The supply is generally affected by inefficient production and poor processing and handling of honey, as well as lack of collaboration among beekeepers for processing and marketing. The challenges in beekeeping in Africa include:
- Low returns from beekeeping – Many farmers have left beekeeping because of lack of profits and low yields and due to the amount of work and the investments that are required for hives and equipment.
- Poor apiary husbandry – Especially in the migratory beekeeping system, but also in fixed apiary system, bees are left to look for their own forage, water and to provide their own security from invaders. During times of scarcity, like dry seasons, hives swarm and abscond and hence the farmer loses potential yield from such hives.
- Pests and diseases – The varroa mite as well as other pests and diseases are threatening beekeeping in Africa, and farmers lack knowledge on their proper management.
- Poor harvesting methods – Rudimentary harvesting methods, for example, using too much smoke or burning the hives leads to destruction of the bee colonies as well as to contamination of the honey harvest.
- Quality control challenges – Due to limited availability and improper use of harvesting equipment, honey becomes susceptible to contamination and adulteration. The resulting low quality honey cannot enter the formal market chain, but ends up in the informal markets being used as an ingredient for making local brews or herbal products. Sanitary requirements have also greatly affected honey export to premium markets.
However, beekeeping is still an important economic activity and a potential source of income for farmers in Africa. It is, therefore, necessary to devise means to improve production and returns from beekeeping.
This chapter on beekeping provides basic information on sustainable and profitable beekeeping and processing.
Discussion – Assessment of the local beekeeping situation
Inquire among the farmers about their knowledge of beekeeping. Have they experienced any of the above or any other challenges? How important is beekeeping to the community? Are bee products commonly in demand?
 tap and then scroll down to the Add to Home Screen command.
tap and then scroll down to the Add to Home Screen command.